Mps1 promotes rapid centromere accumulation of aurora b
scientific report
Mps1 promotes rapid centromere accumulationof Aurora BMaike S. van der Waal1*, Adrian T. Saurin1,2*, Martijn J.M. Vromans1, Mathijs Vleugel1,2,Claudia Wurzenberger3, Daniel W. Gerlich3w, Rene´ H. Medema4, Geert J.P.L. Kops1,2 & Susanne M.A. Lens1+1Department of Medical Oncology, 2Department of Molecular Cancer Research, University Medical Center Utrecht, Utrecht,The Netherlands, 3Institute of Biochemistry, Department of Biology, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology, Zu¨rich, Switzerland,and 4Division of Cell Biology, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Aurora B localization to mitotic centromeres, which is required
The catalytic subunit of the chromosomal passenger complex
for proper chromosome alignment during mitosis, relies on
(CPC), Aurora B kinase, is a key factor for microtubule attachment
Haspin-dependent histone H3 phosphorylation and on Bub1-
error correction and impacts on the mitotic checkpoint
dependent histone H2A phosphorylation—which interacts with
through destabilization of incorrectly attached microtubules,
Borealin through a Shugoshin (Sgo) intermediate. We demon-
strate that Mps1 stimulates the latter recruitment axis. Mps1
formation of the mitotic checkpoint complex required for APC/C
activity enhances H2A-T120ph and is critical for Sgo1 recruit-
inhibition Moreover, Aurora B can also directly stimulate the
ment to centromeres, thereby promoting Aurora B centromere
mitotic checkpoint at the onset of mitosis via kinetochore
recruitment in early mitosis. Importantly, chromosome biorienta-
recruitment and subsequent activation of the checkpoint kinase
tion defects caused by Mps1 inhibition are improved by restoring
Mps1 Finally, Aurora B may also function further
Aurora B centromere recruitment. As Mps1 kinetochore localiza-
downstream in the mitotic checkpoint signalling cascade to
tion reciprocally depends on Aurora B, we propose that this
maintain the APC/C inhibitory signal
Aurora B-Mps1 recruitment circuitry cooperates with the
Similar to Aurora B, Mps1 is also a dual function kinase. It is
Aurora B-Haspin feedback loop to ensure rapid centromere
essential for the mitotic checkpoint and for error correction [
accumulation of Aurora B at the onset of mitosis.
The error correction function of Mps1 has been attributed to the
Keywords: Mps1; Aurora B; biorientation; centromere
phosphorylation of the CPC subunit Borealin that is required for
EMBO reports (2012) 13, 847–854. doi:10.1038/embor.2012.93
Aurora B activation However, Aurora B-independentmechanisms have also been proposed [Therefore it is
unclear exactly how Mps1 promotes error correction.
Localization of Aurora B to mitotic centromeres is important for
When cells divide, duplicated chromosomes face the challenge ofbiorienting on the mitotic spindle to ensure an exact copy of the
efficient error correction. It requires Haspin-dependent phosphor-
genome is passed on to the two newly formed daughter cells.
ylation of histone H3 at Thr3 (H3-T3ph) and Bub1-dependentphosphorylation of histone H2A at Thr120 (H2A-T120ph).
Biorientation is assured through destabilization of erroneous
H3-T3ph binds the Survivin subunit of the CPC and H2A-
kinetochore–microtubule attachments and activation of themitotic checkpoint, which allows time for error correction
T120ph interacts with Borealin through a Shugoshin (Sgo)intermediate The signals upstream of these two
converging centromere recruitment pathways are now beginning
Department of Medical Oncology,
2Department of Molecular Cancer Research, University Medical Center Utrecht,
to emerge. Phosphorylation of Borealin by Cdk1 stimulates the
Universiteitsweg 100, STR 2.129, 3584 CG Utrecht, The Netherlands
interaction between the CPC and Sgo and Aurora B promotes
3Institute of Biochemistry, Department of Biology, Swiss Federal Institute of
its own centromere recruitment by reinforcing Haspin activity
Technology Zu¨rich (ETHZ), HPM D11.3, Schafmattstrasse 18, 8093 Zu¨rich,Switzerland
towards H3-T3ph We show here that Mps1 and Aurora B
4Division of Cell Biology, Netherlands Cancer Institute, Plesmanlaan 121,
cooperate to stimulate the Bub1/H2A-T120ph/Sgo1 recruitment
1066 CX Amsterdam, The Netherlands
axis, which allows rapid centromere accumulation of the CPC at
*These authors contributed equally to this work
the onset of mitosis.
Present address: Institute of Molecular Biotechnology of the Austrian Academy of
Sciences, Vienna, Austria+Corresponding author. Tel: þ 31 88 75 68114; Fax: þ 31 88 75 55430;
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Mps1 is needed to establish Aurora B at centromeresMps1 is required for Bub1 kinetochore recruitment As
Received 1 March 2012; revised 4 June 2012; accepted 5 June 2012; publishedonline 26 June 2012
Bub1-dependent H2A-T120ph is involved in CPC centromere
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012 8 4 7
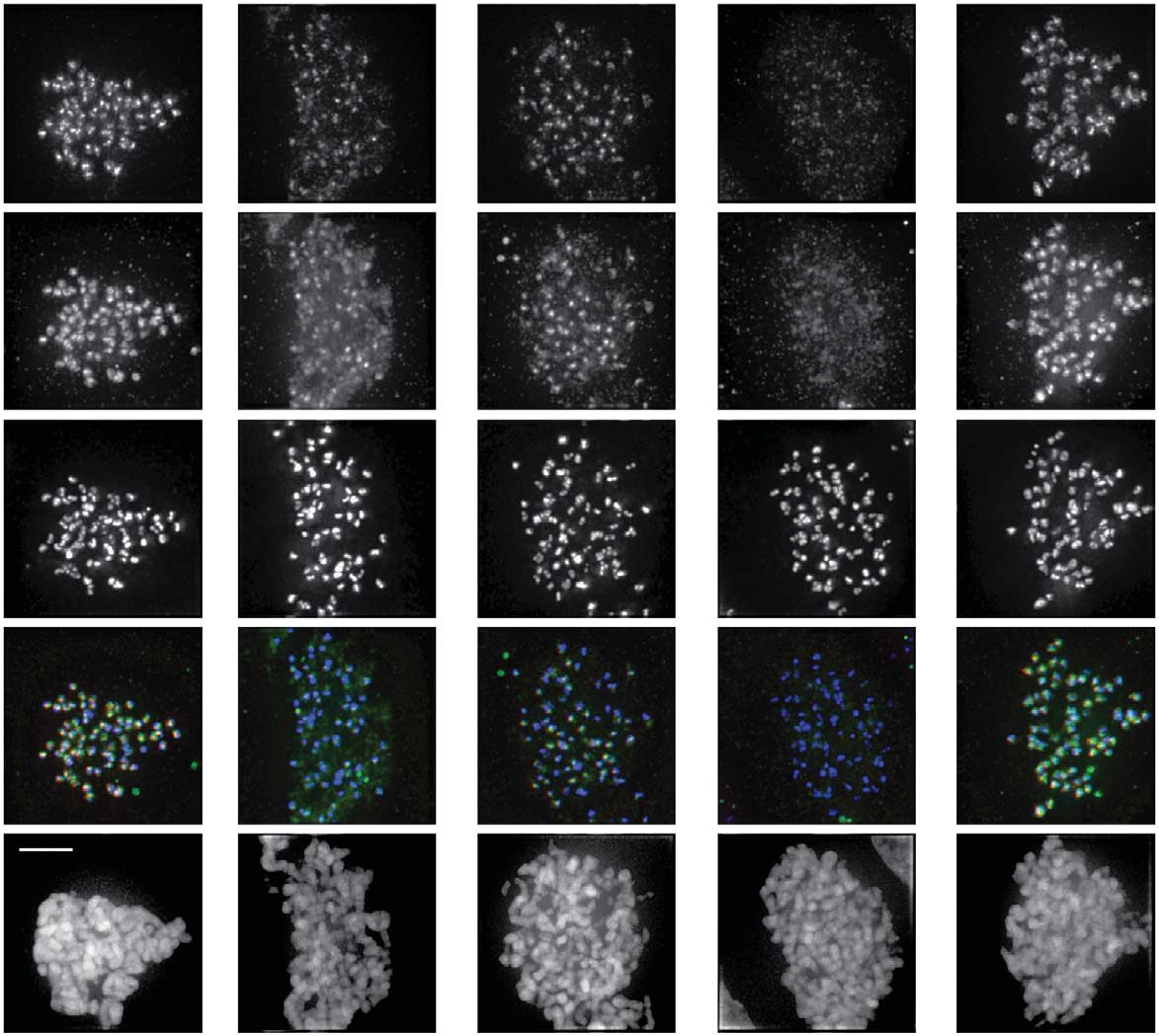
Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora B
M.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
Relative centromere levels
Relative centromere levels
Relative centromere levels
Reversine Mps1-IN-1
Fig 1 Mps1 is required to establish Aurora B centromere localization at the onset of mitosis. All quantifications are signal intensities over CREST(centromere staining). (A) IF and quantifications of Aurora B, Aurora B-T232ph and centromeres (CREST) in HeLa cells. Cells were treated withthe indicated siRNAs (si-Luc ¼ si-Luciferase) for 48 h followed by 30 min treatment with nocodazole and Reversine (1 mM) or DMSO. Early mitoticcells were analysed. Graph represents mean (±s.d.) of 40 cells (Aurora B) or 20 cells (Aurora B-T232ph) per condition, sampled in four or twoindependent experiments, respectively. (B) IF and quantification of Aurora B in U2OS cells treated with nocodazole plus DMSO, Reversine (500 nM) orMps1-IN-1 (10 mM) for 30 min. Early mitotic cells were analysed. Graph represents mean (±s.d.) of 20 cells per condition, sampled in two independentexperiments. (C) IF and quantification of Aurora B in HeLa cells treated with nocodazole and MG132 for 1 h, and DMSO or Reversine (1 mM) foradditional 30 min. Graph represents mean (±s.d.) of 29 cells per condition, sampled in three independent experiments. Scale bars, 5 mm. Forcharacterization of inhibitor concentrations and siRNAs see supplementary Fig S1 online. DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide; IF, immunofluorescence;siRNAs, short interfering RNAs.
recruitment we determined whether Mps1 was needed for
activity was mainly required for the establishment of Aurora B
Aurora B centromere localization. We allowed cells to enter
localization, because if Mps1 was inhibited during mitosis, when
mitosis without Mps1 activity, using the chemical inhibitors
Aurora B had already been accumulated at centromeres, then
Reversine and Mps1-IN-1 or RNA interference (RNAi)-
Aurora B localization was barely affected supplementary
mediated protein knockdown supplementary Fig S1A
Video S1 online).
online). Cells were treated with nocodazole to exclude effects ofkinetochore–microtubule attachments and, as Mps1 inhibition
Mps1 allows rapid Aurora B recruitment to centromeres
silences the mitotic checkpoint (supplementary Fig S1C online),
As Cdk1 activity is important for proper centromere localization of
we only analysed early prometaphase cells recognized by a
the CPC we wanted to test if the defects in Aurora B
dispersed DNA morphology
recruitment upon Mps1 inhibition were related to reduced Cyclin
In the absence of Mps1, Aurora B localized to the chromosomal
B levels owing to checkpoint inactivation. First, we depleted the
arms, instead of accumulating at the inner centromere
checkpoint protein BubR1 and found it had no effect on Aurora B
supplementary Fig S3C online). The fact that Reversine or
localization supplementary Fig S1B,C online). Second, we
Mps1-IN-1 phenocopied Mps1 RNAi indicates that Mps1 activity
used an assay that allowed Aurora B localization to be measured
is required for Aurora B centromere localization The
in the absence of Cyclin B degradation. We adapted the protocol
reduction of centromeric Aurora B corresponded to a decrease in
of Potapova et al and briefly inhibited Cdk1 activity with
Aurora B-T232 autophosphorylation Interestingly, Mps1
RO3306 (RO) in cells arrested in mitosis with the Eg5 inhibitor
8 4 8 EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION

Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora BM.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
Washout (into DMSO/MG132)
Washout (into Reversine/MG132)
t = –15
Centromere levels 0.0
Centromere levels
(+/– inhibitors)
(YFP-YFP/CFP-YFP)
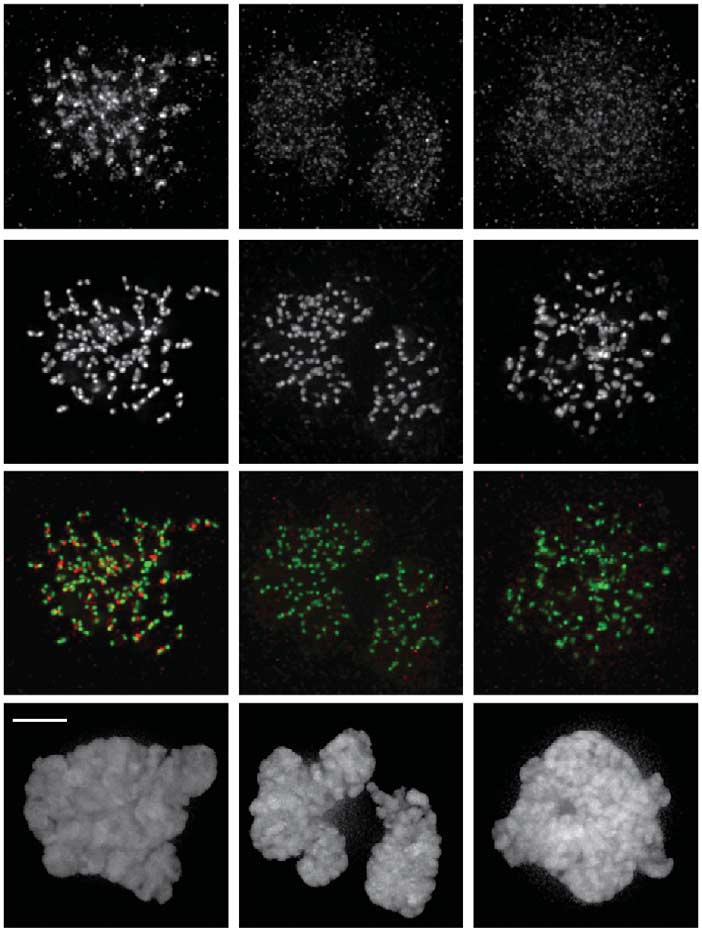
Fig 2 Mps1 inhibition induces a delay in Aurora B centromere accumulation. (A) Schematic depiction of Cdk1 reactivation assay. (B) Time lapseanalysis of Cdk1 reactivation assay in UTR (U2OS stably expressing a Tet repressor) cells expressing wt-INCENP-GFP. Cells were treated as depictedin (A), RO3306 was added after 4 min and washed out after 16 min. Per condition, one representative cell out of eight is shown. (C) IF andquantifications of Aurora B and Aurora B-T232ph in HeLa cells. Cells were treated as depicted in (A), and fixed at indicated time points. Graph showsone representative experiment out of two and represents mean (±s.e.m.) of 10 cells per time point. (D) Time lapse analysis of FRET in U2OS cellsstably expressing a FRET biosensor for Aurora B activity, and treated as depicted in (A). Increased ratio indicates increased FRET sensorphosphorylation. Lines represent means of at least 10 cells (±s.e.m.). Colour-coded images are shown for indicated time points. Scale bars, 5 mm.
CREST, centromere staining; DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide; FRET, fluorescence resonance energy transfer; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IF,immunofluorescence; STLC, s-trityl-l-cysteine.
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012 8 4 9
Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora B
M.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
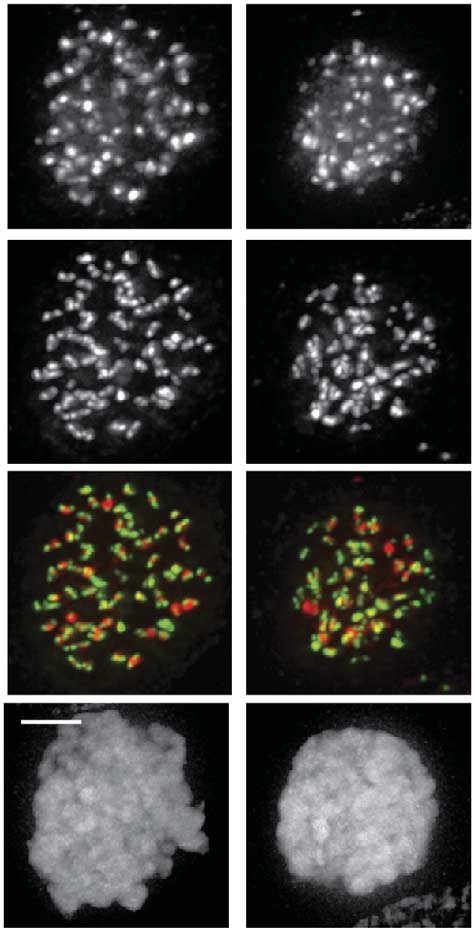
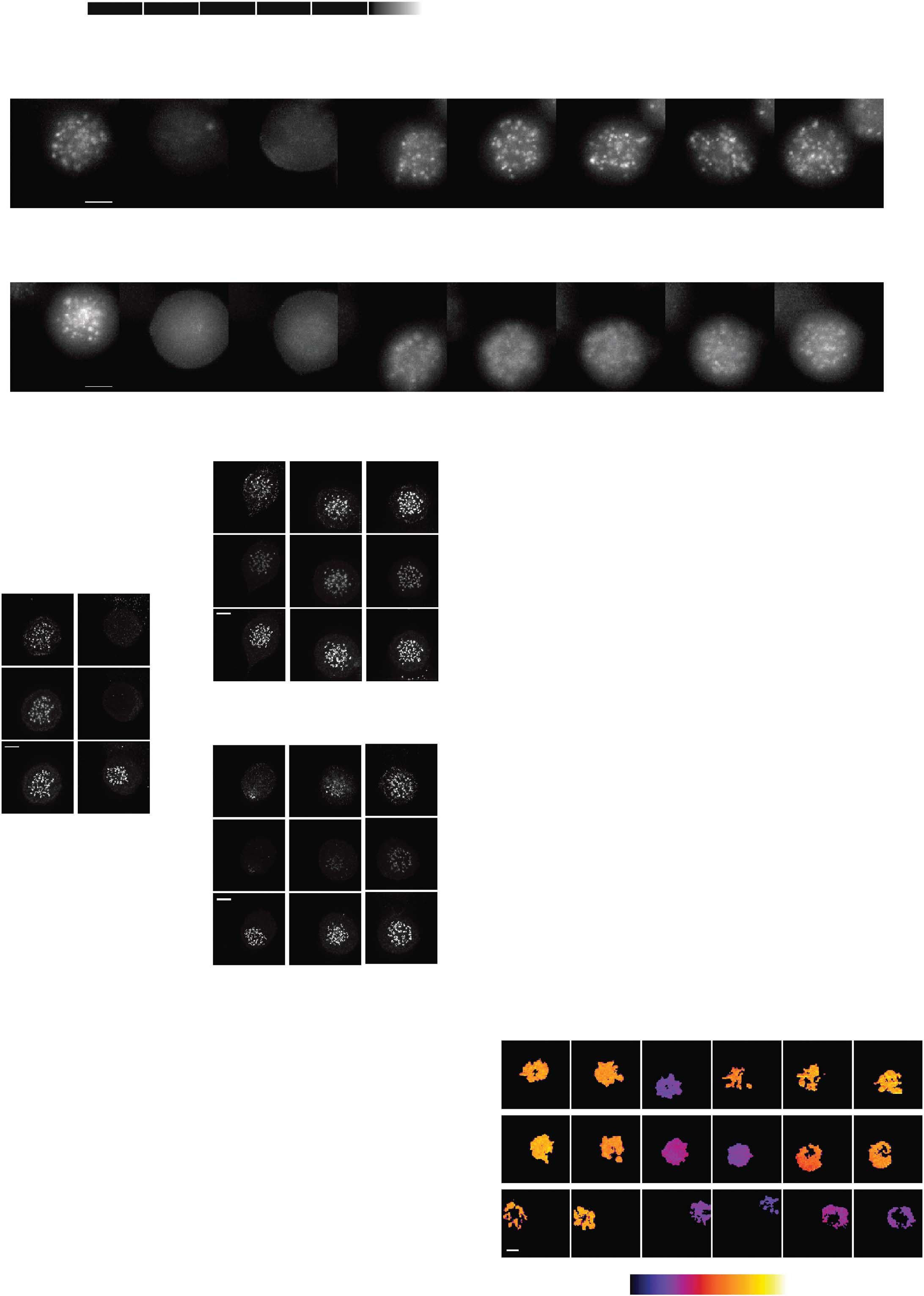
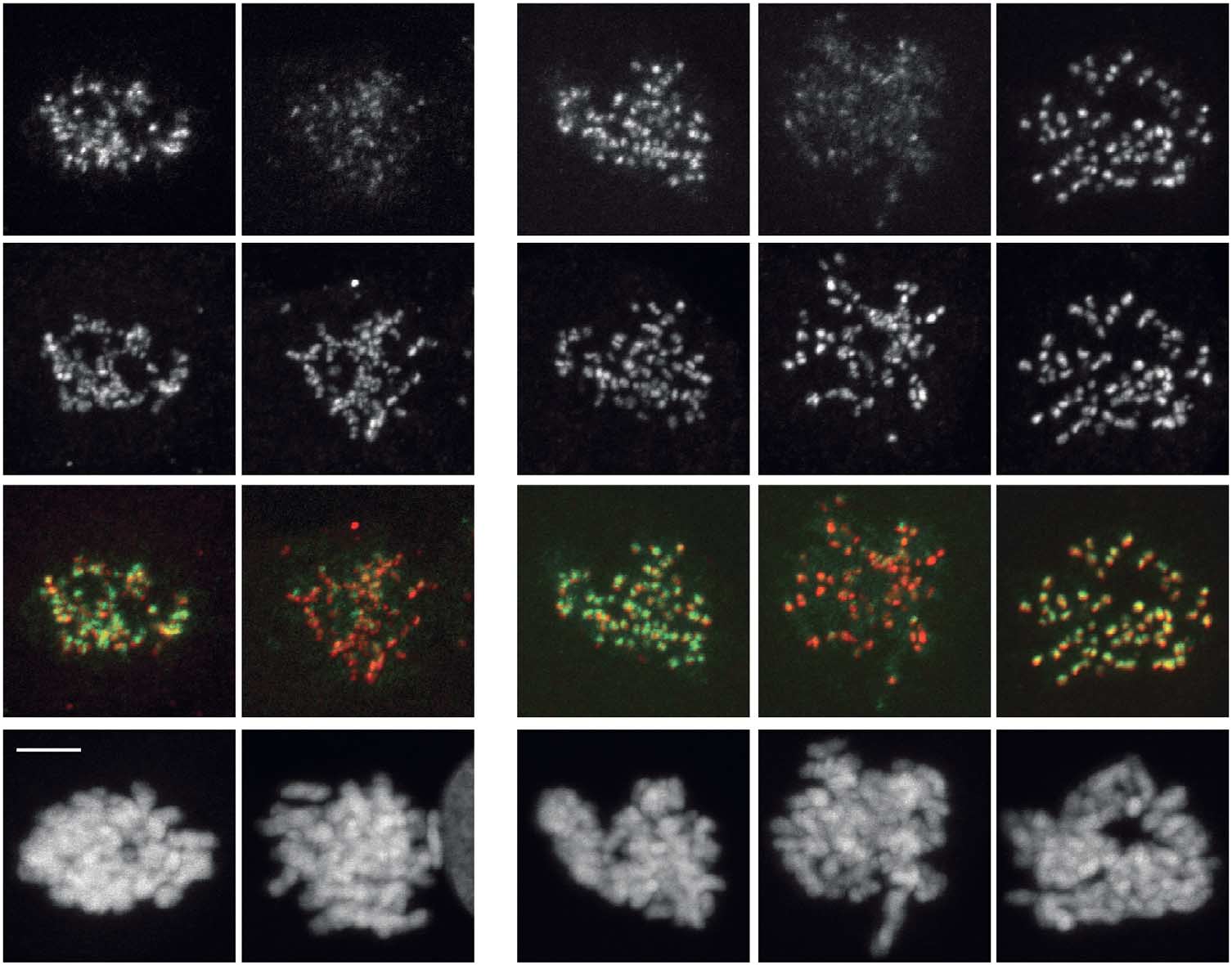
Fig 3 Mps1 regulates the Bub1/H2A-T120ph/Sgo1 pathway for Aurora B centromere localization. All quantifications are signal intensities over CREST
(centromere staining) and early mitotic cells were analysed. (A,B,C) IF and quantifications of Bub1, H2A-T120ph, Sgo1 and centromeres (CREST)in UTR (U2OS cells stably expressing a Tet repressor) cells, and UTR cells expressing CB-INCENP or Mis12-Mps1. Expression was induced withdoxycyclin. Cells were synchronized in G2 with RO3306, released in a medium containing DMSO, Reversine or Hesperadin, and further treated withnocodazole plus MG132 for 30 min. Data represent means (±s.d.) from three independent experiments, each experiment including at least 10 cells percondition. (D) IF of Bub1, Sgo1 and H2A-T120ph in Mis12-Mps1-expressing UTR cells synchronized in G1/S with thymidine and analysed 6 h afterthymidine release (enrichment for G2 cells) in the presence or absence of doxycyclin. (E) IF and quantifications of Aurora B in HeLa cells treated withthe indicated siRNAs for 48 h followed by half an hour treatment with nocodazole and Reversine. Graph shows one representative experiment out oftwo and represents mean (±s.e.m.) of 11 cells per condition. Scale bars, 5 mm. DMSO, dimethyl sulphoxide; IF, immunofluorescence; siRNAs, shortinterfering RNAs; UTR, U2OS cells stably expressing a Tet repressor.
s-trityl-l-cysteine (STLC; in the presence of MG132 to prevent Cyclin
intermediate for CPC recruitment was also affected by Mps1
B degradation) and then allowed return to a mitotic state upon
inhibition. While Sgo2 levels were only slightly reduced, Sgo1
reactivation of Cdk1 (As expected, Cdk1 inhibition resulted
centromere localization was highly sensitive to Mps1 inhibition,
in a rapid removal of ectopically expressed green fluorescent protein
with Sgo1 localizing over the chromosomal arms instead of to the
(GFP)-tagged CPC subunit inner centromere protein (INCEP) from
centromere, much like we observed for Aurora B
centromeres (supplementary Video S2 online, [This
supplementary Fig S3A–C online)
effect of Cdk1 inhibition was reversible because B20 min after RO
We and others have shown recently that Mps1 localization to
washout, the centromere localization of INCENP-GFP was fully
kinetochores is Aurora B-dependent We therefore tested
recovered ; supplementary Video S2 online). When cells
if Aurora B stimulated its own recruitment to centromeres via
were released from Cdk1 inhibition in the presence of Reversine the
Mps1. Aurora B inhibition with Hesperadin caused a reduction in
accumulation of INCENP-GFP at centromeres was significantly
Bub1, H2A-T120ph, Sgo1 and H3-T3ph at kinetochores and
delayed ; supplementary Video S2 online). We confirmed
centromeres, respectively supplementary Fig S3D
these results for endogenous Aurora B in fixed cells and observed a
online). To determine whether this was a consequence of reduced
significant delay in recovery of Aurora B and Aurora B-T232ph when
Mps1 activity, we restored Mps1 localization to kinetochores
Cdk1 was reactivated in the absence of Mps1 activity Note
using Mis12-Mps1 Although, as expected, this did not
that Aurora B did relocalize to centromeres, even in the absence of
restore H3-T3ph (supplementary Fig S3D online), Bub1 kineto-
Mps1 activity, suggesting that Mps1 inhibition merely delays Aurora
chore localization and H2A-T120ph were improved, and Sgo1
B recruitment.
recruitment to centromeres was completely restored
To examine the consequences of delayed Aurora B accumula-
The incomplete rescue of Bub1 kinetochore localization
tion on substrate phosphorylation, we used a chromatin (H2B)-
and H2A-T120ph could indicate that Aurora B also affects
targeted fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET)-based
H2A-T120ph via an additional, Mps1-independent pathway.
biosensor for Aurora B activity that is sensitive to Aurora B
Indeed, we observed an increase of Bub1 kinetochore localization
activity coming from the centromere Treatment of
and H2A-T120ph in the absence of Mps1 activity when Aurora B
mitotic cells with RO/MG132 resulted in decreased sensor
was restored at centromeres by expressing CB-INCENP
phosphorylation, and recovery of Aurora B substrate phosphory-
The complete rescue of Sgo1 recruitment by
lation was delayed when Cdk1 was reactivated in the presence
Mis12-Mps1 in cells with inactive Aurora B suggests that Sgo1 is
of Reversine/MG132, both in U2OS and HeLa cells
under control of Mps1 but only partially via Bub1-dependent H2A-
supplementary Fig S2 online). We noticed that Aurora B-T232ph
T120ph Indeed, when Bub1 kinetochore localization
and sensor phosphorylation were not fully restored in the absence
was restored in cells without active Mps1, using Mis12-Bub1, this
of active Mps1, which could be owing to the requirement of
did not recover Sgo1 localization (supplementary Fig S4A online).
Mps1-dependent Borealin phosphorylation In conclusion,
Moreover, expression of Mis12-Mps1 was sufficient to promote Sgo1
we demonstrate in different cell lines, both fixed and live,
centromere localization in G2 cells even though H2A-T120
that early in mitosis Mps1 promotes Aurora B centromere
phosphorylation was absent . This implies that Mps1 may
recruitment and substrate phosphorylation. The relatively small
also signal directly to Sgo1 as has been suggested recently by others
time window in which Mps1 operates likely explains why the
. Importantly, RNAi-mediated Sgo1 depletion resulted in a
effect of Mps1 on Aurora B centromere localization was not
reduction of centromeric Aurora B to a comparable level as was
previously detected
observed after inhibition of Mps1 indicating that thereduced Sgo1 levels may indeed be responsible for the impaired
Mps1 controls the Bub1/H2A/Sgo CPC recruitment axis
Aurora B centromere recruitment after Mps1 inhibition.
Given the importance of the Bub1/H2A-T120ph/Sgo pathway forCPC centromere localization we rationalized that the defects
Mps1 recruits Aurora B to stimulate error correction
in this pathway could explain the delay in Aurora B centromere
We next tested the significance of the Mps1-Aurora B recruitment
accumulation following Mps1 inhibition. While Mps1 activity
circuitry for error correction, a process that relies on Aurora B and
was dispensable for Haspin-dependent H3-T3ph (supplementary
Mps1 Chromosome alignment was examined upon
Fig S3A,D online), it was indeed required for Bub1 kinetochore
inhibition of Mps1 in stable cell lines with inducible expression of
localization, and H2A-T120ph supplementary Fig S3A
CB-INCENP, which renders Aurora B localization insensitive to
online) in mitotic cells We next determined if the Sgo
Mps1 regulation Cells that had entered mitosis with
8 5 0 EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora BM.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
Relative centromere levels
Relative centromere levels
Reversine Hesperadin
Reversine Hesperadin
Relative centromere levels
Reversine Hesperadin
Relative centromere levels
Mis12-Mps1 H2A-T120ph Merge
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012 8 5 1
Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora B
M.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
% Of mitotic cells
Severe misalignment
Mild misalignment
Complete alignment
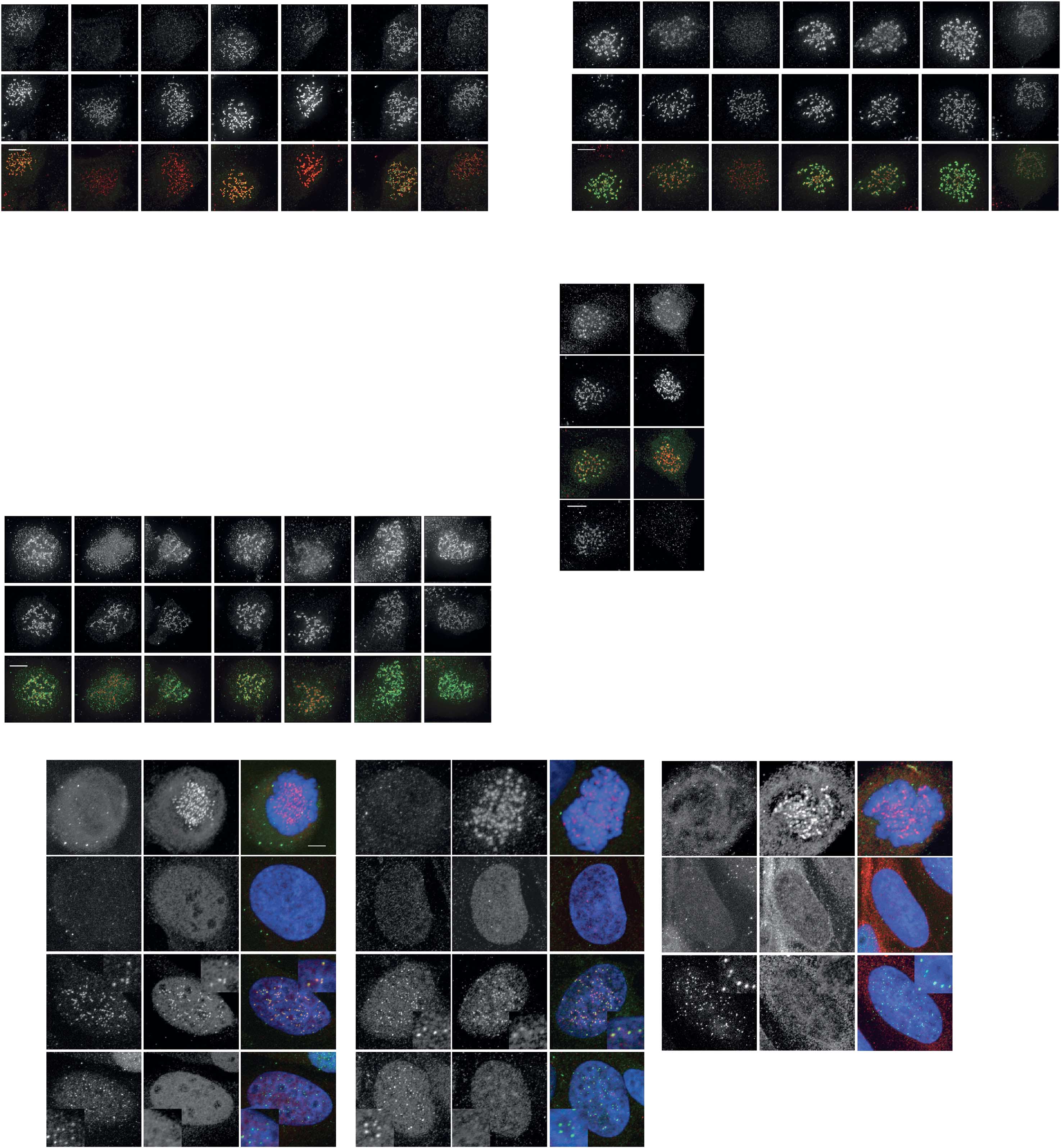
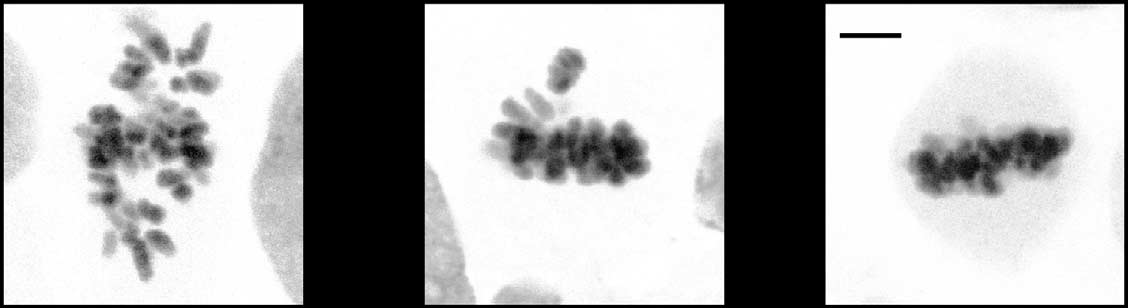
Fig 4 Mps1-dependent Aurora B centromere recruitment promotes efficient chromosome biorientation. (A) IF of Aurora B and centromeres (CREST)in UTR cells with inducible expression of wt-INCENP-GFP or CB-INCENP-GFP. Cells were treated as in (B) Cells were synchronized in G2 withRO3306 and released to enter mitosis in the presence or absence of Reversine for 60 min. MG132 was added for an additional 30 min to accumulatecells in metaphase. Low expression levels of CB-INCENP at the onset of mitosis were accomplished by a relative short protein induction time (6 h).
Graph shows one representative experiment out of two. The number (n) of cells analysed per condition is indicated. Scale bars, 5 mm. (C) Model forthe recruitment circuitries that operate between Mps1-Sgo1-Aurora B (black arrows) and Mps1-Bub1-Sgo1-Aurora B (grey arrows) at the beginningof mitosis to ensure robust establishment of the mitotic checkpoint and error correction machineries. DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; DMSO,dimethyl sulphoxide; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IF, immunofluorescence; UTR, U2OS cells stably expressing a Tet repressor.
active or inactive Mps1 were scored for chromosome alignment
onset of mitosis via centromere recruitment of Sgo1, and we
after 30 min treatment with MG132 to allow sufficient time for
suggest that this recruitment circuitry acts together with the Aurora
alignment in control cells supplementary Fig S4B online).
B-Haspin feedback loop We propose that the mutual
As expected, inhibition of Mps1 reduced the ability of cells to
dependence of Aurora B and Mps1 for the rapid establishment
align their chromosomes. Whereas expression of wt-INCENP did
of Aurora B centromere activity and Mps1 kinetochore activity
not improve alignment under these conditions, we observed a
allows for a fast and coordinated start-up of the error correction and
striking improvement when Aurora B localization to centromeres
mitotic checkpoint machineries so that both processes are fully
was restored by CB-INCENP expression supplementary
functional at the point of nuclear envelope breakdown ).
Fig S4B online). Only mild chromosome misalignments persisted,which might reflect the Aurora B-independent role of Mps1 in
chromosome biorientation
Cell lines and cell culture. Inducible cell lines expressing LAP-Mis12-Mps1D200, wt-INCENP-GFP and CB-INCENP-GFP werepreviously described All inducible cell lines were derived
from U2OS cells stably expressing a Tet repressor (UTR) and
Our data show that an Aurora B-Mps1 regulatory circuitry
cultured in Tet-free medium. Protein expression was induced with
promotes timely and robust Aurora B centromere activity at the
1 mg/ml doxycycline (Sigma-Aldrich) for at least 6 h. HeLa and
8 5 2 EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora BM.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
U2OS cells were transfected with a pIRESpuro2b vector
Ruchaud S, Carmena M, Earnshaw WC (2007) Chromosomal passengers:
containing H2B-targeted FRET sensor for Aurora B activity
conducting cell division. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8: 798–812
Tanaka TU, Rachidi N, Janke C, Pereira G, Galova M, Schiebel E,
and selected with 1 mg/ml puromycin (Sigma-Aldrich) for stable
Stark MJ, Nasmyth K (2002) Evidence that the Ipl1-Sli15 (Aurora
expression. HeLa and U2OS cells were grown in DMEM
kinase-INCENP) complex promotes chromosome bi-orientation by
supplemented with 6% fetal bovine serum, pen/strep and
altering kinetochore-spindle pole connections. Cell 108: 317–329
l-glutamine (2 mM).
Santaguida S, Vernieri C, Villa F, Ciliberto A, Musacchio A (2011)Evidence that Aurora B is implicated in spindle checkpoint signalling
Cdk1 reactivation assay. Cells were incubated for 1.5 h with
independently of error correction. EMBO J 30: 1508–1519
STLC (20 mM, Tocris Bioscience) to arrest cells in mitosis with
Saurin AT, van der Waal MS, Medema RH, Lens SM, Kops GJ (2011)
monopolar spindles. MG132 was added 30 min before addition of
Aurora B potentiates Mps1 activation to ensure rapid checkpoint
RO3306 (10 mM, Enzo Life Sciences). After 10 min, the drug was
establishment at the onset of mitosis. Nat Commun 2: 316
removed by washing the cells with STLC, MG132 (10 mM, Sigma-
Maldonado M, Kapoor TM (2011) Constitutive Mad1 targeting tokinetochores uncouples checkpoint signalling from chromosome
Aldrich) and either dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO), Hesperadin
biorientation. Nat Cell Biol 13: 475–482
(125 nM, Selleck Chemicals), Mps1-IN-1 (10 uM, gift of Dr N.
Abrieu A, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Kahana JA, Peter M, Castro A, Vigneron S,
Grey or Reversine (Sigma-Aldrich, 500 nM for U2OS cells or
Lorca T, Cleveland DW, Labbe JC (2001) Mps1 is a kinetochore-
1 mM for HeLa and UTR cells, supplementary Fig S1A online)-
associated kinase essential for the vertebrate mitotic checkpoint.
containing medium Cells were either fixed at different time
Cell 106: 83–93
points or recovery was imaged live. Details of live and fixed cell
10. Jelluma N, Brenkman AB, van den Broek NJ, Cruijsen CW,
van Osch MH, Lens SM, Medema RH, Kops GJ (2008) Mps1
imaging procedures (including FRET sensor experiments), indirect
phosphorylates Borealin to control Aurora B activity and chromosome
immunofluorescence, antibodies, expression vectors and short
alignment. Cell 132: 233–246
interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are available as Supplementary
11. Maure JF, Kitamura E, Tanaka TU (2007) Mps1 kinase promotes
information online.
sister-kinetochore bi-orientation by a tension-dependent mechanism.
Curr Biol 17: 2175–2182
Chromosome alignment assay. Protein induction was started 3 h
12. Stucke VM, Sillje HH, Arnaud L, Nigg EA (2002) Human Mps1 kinase is
before cells were arrested in late G2 by treatment with RO3306
required for the spindle assembly checkpoint but not for centrosome
(7.5 mM) for 2.5 h. The relative short protein induction time is
duplication. EMBO J 21: 1723–1732
important to ensure that the levels of CB-INCENP are still low
13. Hewitt L, Tighe A, Santaguida S, White AM, Jones CD, Musacchio A,
when cells enter mitosis. Synchronized cells were released to
Green S, Taylor SS (2010) Sustained Mps1 activity is required in mitosisto recruit O-Mad2 to the Mad1-C-Mad2 core complex. J Cell Biol 190:
enter mitosis in the presence of Reversine or DMSO. When cells
entered mitosis (about 1 h after release) they were treated for
14. Maciejowski J, George KA, Terret ME, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Jallepalli PV
30 min with MG132 before fixation.
(2010) Mps1 directs the assembly of Cdc20 inhibitory complexes during
Supplementary information is available at EMBO reports online
interphase and mitosis to control M phase timing and spindle checkpoint
signaling. J Cell Biol 190: 89–100
15. Santaguida S, Tighe A, D'Alise AM, Taylor SS, Musacchio A (2010)
Dissecting the role of MPS1 in chromosome biorientation and the spindle
checkpoint through the small molecule inhibitor reversine. J Cell Biol
We thank A. Janssen for manuscript reading, W. Bruinsma for analyses
help and Dr. Losada and Dr. Grey for reagents. This work was supported
16. Kelly AE, Ghenoiu C, Xue JZ, Zierhut C, Kimura H, Funabiki H (2010)
by the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (Vidi 91766332
Survivin reads phosphorylated histone H3 threonine 3 to activate the
to S.M.A.L. and Vidi 91776336 to G.J.P.L.K.), the Dutch Cancer Society
mitotic kinase Aurora B. Science 330: 235–239
(UU 2009-4311 to S.M.A.L.), the European Research Council (ERC-Stg
17. Wang F, Dai J, Daum JR, Niedzialkowska E, Banerjee B, Stukenberg PT,
KINSIGN to G.J.P.L.K.), the European Communities 7th Framework
Gorbsky GJ, Higgins JM (2010) Histone H3 Thr-3 phosphorylation by
Programme (FP7/2007-2013; n1 241548/MitoSys and n1 258068/Systems
Haspin positions Aurora B at centromeres in mitosis. Science 303: 231–235
Microscopy to D.W.G.) and Boehringer Ingelheim Fonds (C.W.).
18. Yamagishi Y, Honda T, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y (2010) Two histone marks
Authors contributions: M.S.v., A.T.S., G.J.P.L.K. and S.M.A.L. designed
establish the inner centromere and chromosome bi-orientation. Science
the research. M.S.v. and S.M.A.L. wrote the paper with the input of A.T.S.
and G.J.P.L.K. M.S.v. performed most of the experiments and data
19. Tsukahara T, Tanno Y, Watanabe Y (2010) Phosphorylation of the CPC
analysis, with contribution of A.T.S. and M.V. C.W. and D.W.G.
by Cdk1 promotes chromosome bi-orientation. Nature 467: 719–723
generated the FRET sensor vector and the FRET-HeLa cell line.
20. Wang F, Ulyanova NP, van der Waal MS, Patnaik D, Lens SM, Higgins
M.V. generated Mis12-Bub1. R.H.M. contributed financially.
JM (2011b) A positive feedback loop involving Haspin and Aurora Bpromotes CPC accumulation at centromeres in mitosis. Curr Biol 21:
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
21. Sliedrecht T, Zhang C, Shokat KM, Kops GJ (2010) Chemical genetic
inhibition of Mps1 in stable human cell lines reveals novel aspects of
Mps1 function in mitosis. PloS One 5: e10251
Santaguida S, Musacchio A (2009) The life and miracles of kinetochores.
22. Kwiatkowski N, Jelluma N, Filippakopoulos P, Soundararajan M,
EMBO J 28: 2511–2531
Manak MS, Kwon M, Choi HG, Sim T, Deveraux QL, Rottmann S et al
Ditchfield C, Johnson VL, Tighe A, Ellston R, Haworth C, Johnson T,
(2010) Small-molecule kinase inhibitors provide insight into Mps1 cell
Mortlock A, Keen N, Taylor SS (2003) Aurora B couples chromosome
cycle function. Nat Chem Biol 6: 359–368
alignment with anaphase by targeting BubR1, Mad2, and Cenp-E to
23. Potapova TA, Daum JR, Pittman BD, Hudson JR, Jones TN, Satinover DL,
kinetochores. J Cell Biol 161: 267–280
Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2006) The reversibility of mitotic exit in
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A,
vertebrate cells. Nature 440: 954–958
van Meel J, Rieder CL, Peters JM (2003) The small molecule Hesperadin
24. Fuller BG, Lampson MA, Foley EA, Rosasco-Nitcher S, Le KV,
reveals a role for Aurora B in correcting kinetochore-microtubule
Tobelmann P, Brautigan DL, Stukenberg PT, Kapoor TM (2008)
attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint.
Midzone activation of Aurora B in anaphase produces an intracellular
J Cell Biol 161: 281–294
phosphorylation gradient. Nature 453: 1132–1136
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012 8 5 3
Mps1 promotes centromere accumulation of Aurora B
M.S. van der Waal et al
scientific report
25. Wang E, Ballister ER, Lampson MA (2011a) Aurora B dynamics at
27. Liu D, Vader G, Vromans MJ, Lampson MA, Lens SM (2009) Sensing
centromeres create a diffusion-based phosphorylation gradient.
chromosome bi-orientation by spatial separation of Aurora B kinase from
J Cell Biol 194: 539–549
kinetochore substrates. Science 323: 1350–1353
26. Vazquez-Novelle MD, Petronczki M (2010) Relocation of the
28. Storchova Z, Becker JS, Talarek N, Kogelsberger S, Pellman D (2011)
chromosomal passenger complex prevents mitotic checkpoint
Bub1, Sgo1, and Mps1 mediate a distinct pathway for chromosome
engagement at anaphase. Curr Biol 20: 1402–1407
biorientation in budding yeast. Mol Biol Cell 22: 1473–1485
8 5 4 EMBO reports VOL 13 NO 9 2012
&2012 EUROPEAN MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ORGANIZATION
Outline placeholder
Outline placeholder
Source: http://systemsmicroscopy.eu/sites/default/files/Systems%20Microscopy/Publications-pdf/van%20der%20Waal%20et%20al.,%202012.pdf
Paediatric rhinitis: position paper of the EuropeanAcademy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology G. Roberts1,2, M. Xatzipsalti3, L. M. Borrego4,5, A. Custovic6, S. Halken7, P. W. Hellings8,N. G. Papadopoulos9, G. Rotiroti10,11, G. Scadding10, F. Timmermans12 & E. Valovirta13 1David Hide Asthma and Allergy Research Centre, St Mary's Hospital, Isle of Wight; 2NIHR Respiratory Biomedical Research Unit,University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust and University of Southampton Faculty of Medicine, Southampton, UK; 3First
Aesthetic Surgery Journal Office-Based Anesthesia: Dispelling Common Myths Aesthetic Surgery Journal The online version of this article can be found at: can be found at: Aesthetic Surgery Journal Additional services and information for Office-Based Anesthesia: Dispelling Common Myths Douglas R. Blake, MD














