Thesis proposal meeting
December 5, 2014
Emerging Strategies for the Immunotherapy of Pancreatic Cancer
Elizabeth M. Jaffee, M.D. Dana and Albert Broccoli Professor of Oncology Skip Viragh Pancreatic Cancer Center Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center at Johns Hopkins
Disclosure Information
Elizabeth M. Jaffee, M.D.
I have the following financial relationships to
disclose
I will be discussing the investigational use of:
GVAX Listeria Monocytogenes – mesothelin
Both licensed to Aduro Biotech with potential to
receive royalties
Cancer Immunotherapy Comes of AGE
• FDA approved a prostate cancer vaccine (
sipuleucel-T)
targeting a specific cancer antigen
• FDA approved a checkpoint inhibitor ipilimumab targeting
the T cell inhibitory signal CTLA-4
• PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blockade agents are showing
efficacy in solid tumors
• FDA approved the first PD-1 blocking antibody
pembrolizumab for ipilimumab resistant melanoma
What have we learned from these successes?
Immune checkpoints are the game changer!
Immune checkpoint agents act on T cells
Only a minority of tumors have natural T cells
50% of melanomas
10-20% lung and colorectal tumors
For most cancers immune modulation alone is not
enough – a T cell generating agent is also needed
More studies are needed to better understand all of the
inflammatory signals involved in regulating immune
responses within each tumor's microenvironment
Single agent vaccines/immune checkpoints not enough
even for "immunologic" cancers! We still have lots of room
for improvement!
Provenge: Compared with placebo
Yervoy: Yervoy vs. GP100
in metastastic patients
vacine vs. Yervoy + GP100 vaccine
Autologous PBL exposed to
cytokines and antigen
GP100=antigenic peptide vaccine
50% of Melanomas have spontaneous
infiltration of effector T cells
Explains why immune checkpoint inhibitors
work more often in this cancer without vaccines
Combinations are needed to achieve the full potential of
the immune system to recognize and kill all cancers
• Vaccines are the most efficient way to induce T cells
• Understanding all of the signals that regulate immune
responses to the different cancers will determine the best combinations
Immune-Modulatory Receptors & Ligands Regulating T Cells: Emerging
and in the Clinics
PD-L1/PD-L2
B7.1/B7.2
B7RP -1 ICOS
B7-H5 CD28H
Tumor Cell or
MHC/pep TCR
Dendritic Cell
CD137L CD137
OX40L OX40
LIGHT LIGHT-R
CD40 CD40L
PS/galectin9 Tim3
CD200R CD200
Biologic roles NOT redundant
Differential up-regulation by different tumor types
The inflammatory response in theTME is a progressive, dynamic
process, interrelated with cancer genetics
Telomere
mesothelin
Shortening
mutation
Cyclin D1
DPC4
BRCA2
KEY POINTS
These new "immune checkpoint" agents act on T cells For most cancers immune modulation alone is not
enough – a T cell generating agent is also needed
Different cancers may have different checkpoint
pathways that predominate
BALAN LAN
G TO INOGENIC
NOT AN ALL OR NONE SITUATION!
RES FAVOR
CANCER GROWTH
What makes immunologically quiescent
tumors different from immunologically
active cancers like melanoma that
respond to immunotherapy?
The Prototype of Immunologically Quiescent Tumors
Pancreatic
National Cancer Institute: SEER Survival Monograph
Effector T cell infiltration NOT usually a natural
response to cancers like pancreatic cancer
But even in cancers like pancreatic cancer the immune system can be provoked!
A dendritic cell recruiting vaccine provokes T cells: 2 genetically
modified allogeneic tumor cell lines expressing GM-CSF
Jaffee, et al., Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2001, Laheru, et al., Clinical Cancer Research, 2008 Emens et al, Journal of Clinical Oncology 2009, Lutz, et al., Annals of Surgery, 2011.
(Neo)adjuvant Pancreatic Cancer Vaccine Study Provides
New Evidence for ANTITUMOR Immunity
Cancer Immunology Research, 2014
ide to deplete Tregs
Adjuvant Chemoradiation
3rd Vaccine 5th Vaccine
and Chemotherapy
Arm A: Vaccine alone Arm B: Vaccine + low dose IV Cy Arm C: Vaccine + metronomic Cy
Lei Zheng, M.D./Ph.D. Chris Wolfgang M.D./Ph.D. Dan Laheru, M.D. Eric Lutz, Ph.D.
Lymphoid Aggregates found in 2 location patterns
in vaccinated patients 2 weeks after a single vaccine
Lymphoid aggregates in PDAs are composed of organized
T and B cell zones and a Germinal Centre-like structure
Lymphoid aggregates are composed of
myeloid-derived antigen-presenting cells
Development of lymphoid aggregates
involves lymphoid neogenesis
Lymphatic vessel marker
Chemokine involved in
lymphoid Neogenesis
Lymphoid Aggregates Are Sites of Immune
Activation and Regulation – Not Cytoloysis
PD-1/PD-L1 pathway is upregulated in
vaccine induced lymphoid aggregates
Foxp3+ cells are decreased and Teff/Treg ratios are
T cells can also be found infiltrating
increased in non-aggregate intratumoral areas of
between lymphoid aggregates
PDAs from patients with OS>3 yr vs <1.5 yr
Foxp3/area TA OS>3 vs. <1.5
s.<1.5 yr
Foxp3+ T cells
CD8+ T cells/Foxp3+
Microdissection and microarray analysis of
intratumoral lymphoid aggregates from
responders vs non-responders identifies gene
signatures associated with response
Decreased Tregs - increased Th17 - decreased
PDL1 correlate with improved survival
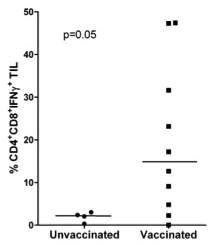
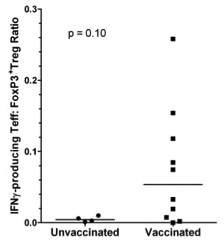
Vaccination induces increased numbers of IFNγ
producing T cells infiltrating the tumor
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells
CD8+/FoxP3+ T cells
Vaccines can induce tumor Infiltrating lymphocytes in
traditionally "non-immunogenic" tumors
• Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in turn secrete IFNg and other cytokines that upregulate the PD-1/PD-L1 and other immune modulating pathways • But vaccine induced infiltrating T cells likely get down regulated by suppressive mechanisms within the tumor – (PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4 and others) • Vaccines must be given with agents that modulate these suppressive mechanisms to activate the T cell response
Clinical study supporting the need for combining
a T cell activating vaccine with T cell modulating
agents in pancreatic cancer patients
Dr. Dung Le
Phase Ib: Ipilimumab 10 mg/kg Alone or Ipi + Vaccine
Le, et al., J Immunother 2013
INDUCTION PHASE
MAINTENANCE PHASE
•Vaccine = 2.5 x 108 Panc 6.03 + 2.5 x 108 Panc 10.05 tumor cells
•*Tumor assessments (TA)
•Maintenance Phase Dosing And/Or TA q 12 weeks if SD or better at Week 22
Ipilimumab + Vaccine Improves Survival In Advanced Pancreatic Cancer Patients
Projected Survival Curves 12/1/2011
Median OS = 5.5 vs 3.3 Mos (p=0.14)
GVAX/ipi (n=15) 10 Mos Survival = 45% vs 7%
log-rank, p = 0.068
median OS = 5.5 vs 3.3 mos
12 mos OS = 27% vs 7%
• Metastatic patients having failed >2 chemotherapies • Phase II multicenter study under development • 7/15 patients in combo arm with clinical and/or biomarker response • 0/15 in single Ipi arm with clinical and/or biomarker response
Radiographic Regressions After 14 Weeks
Of Treatment with Ipilimumab (Ipi) + Vaccine
Baseline
Week 7
Ipi/Vaccine
Week 14
Ipi/Vaccine
CA19.9 Changes with Ipilimumab+vaccine treatment
8.016 ALB
8.018 GNO
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65
Time (weeks)
Time (weeks)
Remains on study with
No progression at 65 weeks
For hypophysitis
Off steriods but no further treatment No progression as of 75 weeks with declining CA19.9
ON THE HORIZON
• New vaccine approaches to induce better T cells
Listeria monocytogenes targeting tumor antigens
DNA, peptide, DC, Listeria platforms delivering individual patient specific mutations
• Combinations of immune checkpoint inhibitors with
Anti-CTLA-4 + GVAX vaccine (enrolling)
Anti-PD-1 + GVAX prime/Listeria Boost (Initiation Dec 9, 2014)
• Combinations of immune activating agents with
methylation targeting agents or radiation
Both uncover antigens and inflammatory signals within the tumor micro-environment
• Engineered T Cells (CARS) that target GI cancer tumor
TWO VACCINES MAY BE BETTER THAN ONE!
PRIME/BOOST STUDY – 2 synergistic mechanisms
GVAX Pancreas
LADD Listeria
Irradiated, whole-cell tumor vaccine
Live-attenuated Listeria monocytogenes
ΔactA ΔinlB
Antigen uptake
Tumor Cell
& Activation
Destruction
LADD Vaccine expressing Mesothelin
Key Features
• Complete deletion of 2 virulence
genes (actA, inlB)
• Mesothelin expression cassette
ΔactA ΔinlB
stably inserted into the chromosome at inlB locus
• No antibiotic resistance genes
• Antigen expression/secretion
induced inside APCs
actA promoter
ActAN100
• Induction of robust innate and
Mesothelin
antigen-specific adaptive immunity
Preclinical Data Supporting GVAX as Prime and Listeria as Boost Vaccine
RESULTS: Phase 2 Trial: Multi-Center,
Open-label, Randomized, Controlled
Le et al, GI ASCO 2014; Oral Abstract #177
Le et al, Journal of Clinical Oncology, in press
Subjects with
24 months follow-up
metastatic
pancreatic
* Additional courses
20-wk treatment Course*: 6 doses, q3w
if clinically stable
cancer; failed
R Arm B, n=30
or refused
24 months follow-up
• Primary objective: overall survival
• 80% powered to detect a difference of 3.1 months (5 to 8.1 months)
(alpha = 0.15, 1-sided)
• Secondary objectives: safety, immune & clinical responses
Improved OS in
Improved OS in
GVAX/CRS-207 Combo
GVAX/CRS-207 Combo
All Patients
3rd Line Patients
p=0.0003 (one-
HR 0.5930
HR 0.2957
Median OS
Arm A: 6.1 months
Median OS
Arm B: 3.9 months
Arm A: 5.7 months
Arm B: 3.9 months
Dung Le, et al. and AduroBiotech: Abstract # Oral Abstract #177
Follow up study enrolling nationally
Le, et al., Journal of Clinical Oncology, in press
Percent Change From Baseline in the CA19.9 Biomarker
Ongoing studies to address critical questions
• 3 arm study comparing prime/boost vs Listeria-mesothelin vs SOC
Randomized 1:1:1
240 metastastic patients who failed 2nd or 3rd line chemotherapy
23 sites in US
• Chemotherapy versus GVAX/ipilimumab in FOLFIRINOX stable patients
Randomized 1:1
42 patients per arm
3 sites in US
• Prime/boost vs prime/boost + anti-PD-1 mAb (Nivolumab)
Randomized 1:1
88 patients who failed 1 prior chemotherapy
5 sites in US
Begins enrolling January 2015
FINAL POINT:
Improving Survival with Combination Therapy
Combination
Checkpoint Blockade
Standard
Combinations needed for the big therapeutic leap!
Lei Zheng
Clinical Research
Eric Lutz
Barish Edil
Chris Wolfgang
Dan Laheru
Ralph Hruban
Raka Bhattacharya
Viragh Pancreatic Cancer Center
Increased Th17A expression in lymphoid
aggregates confirmed by FACS and IHC
Source: https://ruesch.georgetown.edu/sites/ruesch/files/files/upload/12-5-%20Presentation%207%20-Jaffee%20Friday.compressed%20small.pdf
Die Geburten meiner zwei Töchter – einmal ohne und einmal mit Traude. Kein Vergleich! BEL und Sophie Licht! Die Schwangerschaften Ich habe zwei gesunde Kinder (Sophie-Therese 2003, Amelie-Louise 2006) zur Welt gebracht und dennoch lässt sich dieses Kapitel ganz kurz halten: ich bin/war sehr gerne schwanger! Ich konnte es jedes Mal unheimlich genießen
Inscrita el 11/10/2001 con el número 255 en el Registro de ICC Extranjeras de la CNMV MEDIOLANUM INTERNATIONAL FUNDS LIMITED (Sociedad Gestora) RBC DEXIA INVESTOR SERVICES BANK S.A., DUBLIN BRANCH ESCRITURA DE TRUST MODIFICADA Y REFUNDIDA (un fondo de inversión en régimen fiduciario ("unit trust"). DILLON EUSTACE SOLICITORS









