Comparison of pepck gene expression during reproductive development of chickpea plant (cicer arietinum l
Journal of Cell and Molecular Research (2013) 5 (1), 24-34
Molecular docking approach of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors for identifying
new potential drugs: Insights into drug-protein interaction discovery
Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, Shahrekord University, Shahrekord, Iran
Received 16 August 2013 Accepted 14 September 2013
Abstract
Monoamine oxidase (EC, 1.4.3.4) or amine oxidoreductase catalyzes the oxidative deamination of biogenic
amines. Abnormal action of the monoamine oxidase B has been associated with neurological dysfunctions including parkinson´s disorder. Monoamine oxidase B inhibitors divulged that these agents were effective in the therapeutic management of Parkinson's disease. Understanding the interaction of monoamine oxidase binding site with inhibitors is crucial for the development of pharmaceutical agents. At the molecular docking, the exact prediction of the binding modes between the inhibitors and protein is of central importance in structure-based drug design. In the current study, we examined two classes of monoamine oxidase B inhibitors. We applied Autodock tools 4.2, in order to set up the docking runs and predict the inhibitors binding free energy. The final product of molecular docking was clustered to specify the binding free energy and optimal docking energy conformation that is investigated as the best docked structure. Docking results indicate that the contribution of van der Waals interactions is greater than electrostatic interactions so that, it can be concluded that all of the inhibitors attached to a hydrophobic binding site in monoamine oxidase B. Among the total of molecules tested, it was proved that 2-(2-cycloheptylidenehydrazinyl)-4-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazole has the lowest binding free energy and the lowest Van der Waals energy and also the lowest inhibition constant and subsequently the most experimental affinity. As well as, we find out a possible relationship between the estimated results and experimental data. The selective information from this work is crucial for the rational drug design of more potent and selective monoamine oxidase B inhibitors based on the 8-benzyloxycaffeine scaffold.
Keywords: monoamine oxidase B inhibitor, Parkinson´s disorder, molecular docking, binding free energy
Introduction
and phenylethylamine and is inhibited by deprenyl
Monoamine oxidase (EC, 1.4.3.4) or amine
Abnormal action of the monoamine oxidase B
oxidoreductase is a mitochondrial bound enzyme
isoform has been associated with neurological
dysfunctions including parkinson´s disorder and
monoamine oxidase catalyzes the oxidative
alzheimer´s disorder whereas the monoamine
oxidase A isoform seems to be associated with
exogenous amines, dietary amines, hormones,
psychiatric considerations including depression and
dopamine, serotonin and neurotransmitters
cardiac cellular degeneration
. Furthermore, reports have described that the
. Therefore, monoamine oxidases are virtually
level of monoamine oxidase B in human beings
associated with higher brain functions. Two
raises four to five fold throughout aging and results
isoforms of monoamine oxidases have been
in an increase in catalytic reaction products such as
described, i.e. monoamine oxidase A and
hydrogenperoxide and a decrease in certain
monoamine oxidase B. Before their molecular
neurotransmitter levels
characterization, the differences between these two
. Monoamine oxidase
isoforms were determined on the basis of substrate
B inhibitors, such as D-deprenyl (selegiline)
and inhibitor sensitiveness. Monoamine oxidase A
divulged that these agents were effective in the
therapeutic management of Parkinson's disease.
norephinephrine and serotonin and is inhibited by
The rationale utilization of monoamine oxidase B
inhibitors in parkinson's disorder is based on the
selectively catalyzes the oxidation of benzylamine
monoamine oxidase B. Inhibition of monoamine
Corresponding author E-mail:
oxidase B about an increases the dopamine, and
[email protected]
low levels of dopamine is associated with
Molecular docking approach of monoamine oxidase B …
parkinson´s disease. Age related additions in
heavily based on or influenced by structure-based
drug design and screening strategies.
neuroprotective impressions of its inhibitors, have
In the present work, our purpose was to
been studied as rational bases to apply monoamine
distinguish correct poses of inhibitor in the binding
oxidase B inhibitors in alzheimer's disorder
pocket of monoamine oxidase B and to predict the
affinity between the inhibitor and monoamine
. Regrettably, the usage of monoamine
oxidase B. In other words, in this study docking
oxidase inhibitors might be confined, although they
procedure describes a process by which two
are often last line treatment, in some cases, by
molecules fit together in three-dimensional
adverse effects such as those related to the co-
space . At the molecular
administration of certain diets or drugs, which can
docking, the exact prediction of the binding modes
lead to serious hypertensive and hyperpyretic crises
between the inhibitors and protein is of central
. Hence, tremendous
importance in structure-based drug design
attempts have been undertaken to discover new
pharmaceutical agent that are linked to monoamine
Ligand structure
monoamine oxidase B inhibitors is a great interest
Due to the special characteristics of monoamine
in drug discovery .
oxidase, the researchers have focused on various
Materials and Methods
Understanding the interactions of monoamine
oxidase binding site with inhibitors are crucial for
. Since, some of these were the effective
inhibitors against the monoamine oxidase B it may
Computer aided drug design is an applicable
be a potential therapeutic agent for parkinson´s
method that can study these interactions and
disease. Therefore, we select some of the potent
describe significant characteristics for monoamine
oxidase binding site recognition
monoamine oxidase B
. In the current study, we
docking is widely applied for approximation of bio
examine two classes of monoamine oxidase B
molecular complex and in order to analyze the
inhibitors; these two classes of inhibitors are 2-(2-
structure-function processes and the bio molecular
cycloheptylidene
design. Drug design is the other application of
docking. The precise interaction of agents or
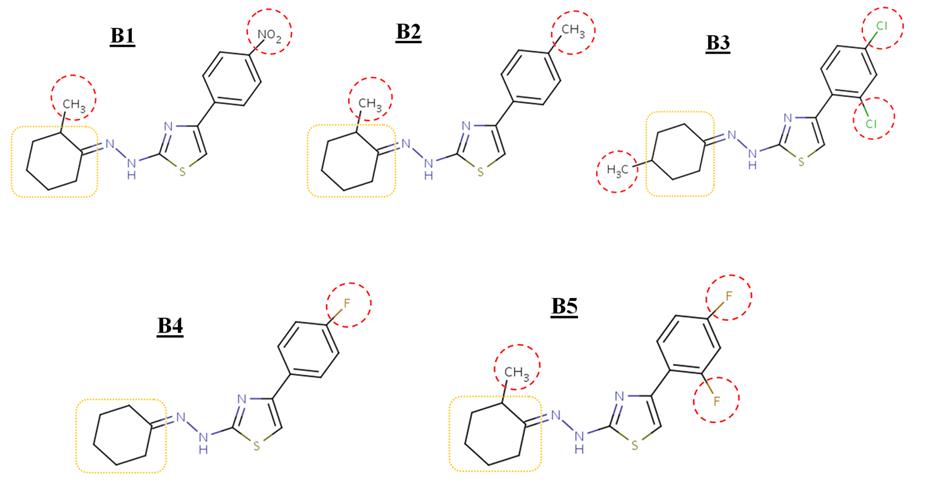
benzyloxycaffeine analogues). Figure 1 shows the
candidate molecules with their targets is crucial in
structure of inhibitors A1-A6 and figure 2 shows
the developmental procedure. Docking is applied to
the structure of inhibitors B1-B5.
predict the binding orientation of small molecular
In the present study, molecular modeling of the
drug candidates to protein targets, subsequently
inhibitors was carried out using Hyperchem 7
predicting the affinity and activity of the drug
software. Hyperchem 7 was employed to draw and
optimize the structure of inhibitors
. In addition, docking is often
For all initial structures geometric optimization
applied to predict binding affinities of drug
calculations by use of molecular mechanics were
candidates in virtual screening experiments and in
performed and afterward the lowest energy
structure-activity
conformers were optimized using the semiempirical
prioritize synthesis of new drugs .
PM3 method, the conjugate gradient and steepest
Docking of the small molecules into the structures
descent algorithm. At the end these structures
of macromolecular targets and scoring their
converted to .pdb format by Hyperchem 7 software.
potential complementarity to binding site is widely
Optimized inhibitor structure was used as input file
applied in hit recognition new drugs. Indeed, there
are a number of drugs whose development was
Journal of Cell and Molecular Research
Figure 1. Structure of inhibitors A1-A6. [A1] 2-(2-cycloheptylidenehydrazinyl)-4-phenyl-1,3-thiazole, [A2] 2-(2-
cycloheptylidenehydrazinyl)-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-thiazole,
Figure 2. Structure of inhibitors B1-B5. [B1] 2-[(2E)-2-(2-methylcyclohexylidene)hydrazinyl]-4-(4-nitrophenyl)-1,3-
thiazole,
Protein structure
resolution was received from the Protein Data Bank
In the current study, the protein X-ray crystal
and was used as the receptor starting structure. This
structure of human monoamine oxidase B with
structure comprised a dimeric form of the human
1OJA code and X-ray diffraction at 1.70 Å
monoamine oxidase B, with each chain interacting
Molecular docking approach of monoamine oxidase B …
combined with a local search) with population size
codenamed ISN (isatin or indol-2,3-dione) and
of 150. Monoamine oxidase B kept rigid in docking
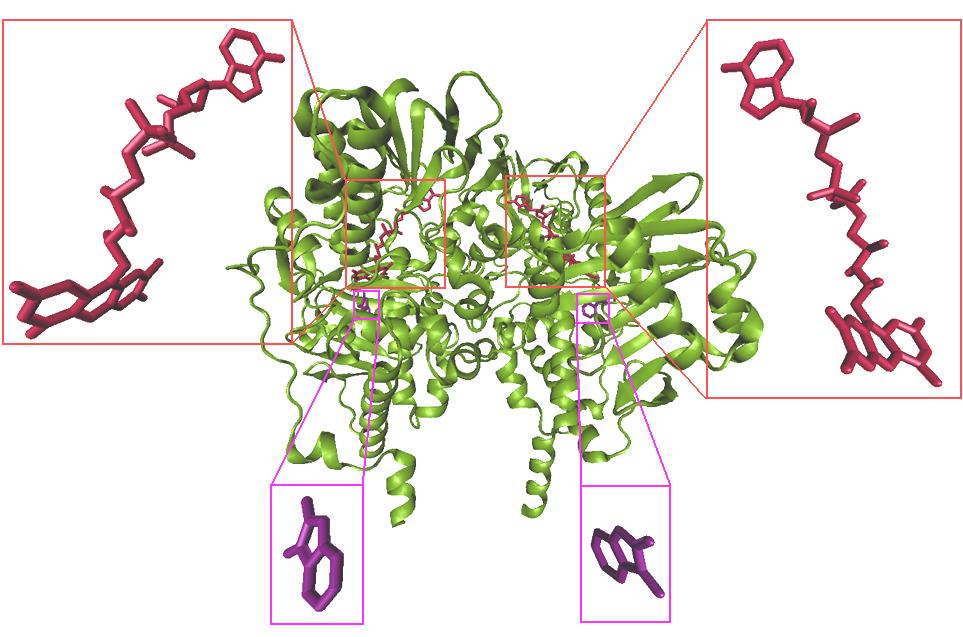
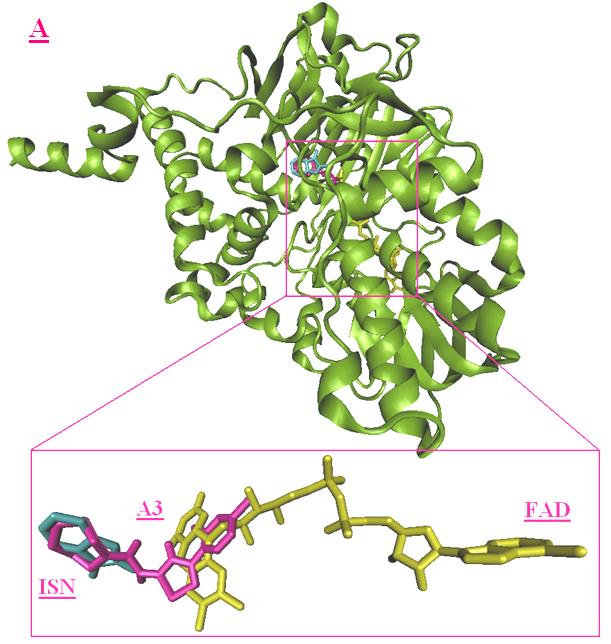
several water molecules. Figure 3 shows the x-ray
process. The inhibitor structures were attributed
crystal structure of monoamine oxidase B in
flexible. In other words all the inhibitors rotatable
complex with inhibitor ISN and FAD. For docking
bonds were adjusted in fewest atoms; note also that
process, only the coordinates of chain A and FAD
cyclic rotatable bonds are excluded. The other
were considered as the receptor structure, and the
co-crystallized inhibitor was removed for the
parameters, except for the step size parameters that
docking studies. The presence of cofactors revealed
were chosen to be 0.2 (translation) and 5.0 degrees
to be essential for the definition of the docking site.
(quaternion and torsion). Finally, by setting all the
We applied Autodock tools 4.2, in order to set up
parameters, inhibitors were docked to the
the docking runs and predict the inhibitors binding
monoamine oxidase B
Docking protocol
AutoDockTools contain a number of methods for
In the current study, AutoDockTools 4.2 was
considering the results of docking simulations,
applied for docking process. AutoDockTools 4.2
uses a grid-based approach in order to allow
exploring of the large conformational space
conformations, visualizing interactions between
available to drug candidate around an embedded
ligands and proteins. At the end of a docking
protein in a grid, as well as to provide rapid
process, AutoDock writes the data on clustering
evaluation of the binding energy of drug candidate
and binding energies to the log file. The docking
conformations. A probe atom is consecutively
results were clustered with 2 Å root mean square
located at each grid point, the interaction energy
deviation and were ranked according to the
between the probe and the target protein is
estimated binding free energy. The structure with
estimated, and the value is stored in the grid. This
proportional lower binding free energy and the
grid of energies may then be applied as a lookup
most conformation in cluster was selected for the
table during the docking simulation
optimum docking conformation .
.
The intensity of the interaction between the
AutoDockTools 4.2 was employed to docking
inhibitor and the receptor can be evaluated
process of inhibitors to monoamine oxidase B
experimentally and is often described as the
. Initially, all of the polar
dissociation constant, Kd, or by the concentration
hydrogens were added to the inhibitors and
of inhibitor that inhibits activity by 50%, the IC50.
Gasteiger-Marsili atomic partial charges were set
The binding free energy is the thermodynamic
for them, and all the inhibitors rotatable bonds were
quantity that is determined by equation 1 and is of
adjusted in fewest atoms. The final inhibitor
interest in computational structure-based design
structures were saved in .pdbqt format. Then polar
hydrogen was added to the protein crystal structure
and the kollman atomic partial charge was set for
Equation 1
monoamine oxidase B. The final protein structure
was saved in .pdbqt format. An extended pdb format, called pdbqt, is applied for coordinate files,
The relationship between the binding free energy
which include atomic partial charges and atom
∆G and the experimentally determined Kd or IC50
types; pdbqt files as well include data on the
is demonstrated in equation 2.
torsional degrees of freedom .
Grid box was created by Autogrid 4 with 30 × 30 ×
Equation 2
30 Å in x, y and z directions with 0.375 Å spacing
and center of box was located on the active site
The interactions between the inhibitor and the
according to co-crystallized inhibitor coordination.
receptor also can be measured by means of
The monoamine oxidase B active site was easily
AutoDock 4.2. In the present work, our purpose
distinguished as the hydrophobic cavity comprising
was to attain an agreement between the docking
the co-crystallized ligand ISN. The genetic
results and experimental data.
algorithm was used to determine the probable
The AutoDock 4.2 force field is designed to
accommodate for each inhibitor to monoamine
estimate the binding free energy of inhibitors to
protein. It includes an updated charge-based
Lamarckian genetic algorithm (Genetic Algorithm
Journal of Cell and Molecular Research
desolvation term, advances in the directionality of
11.54 kcal/mol). The more negative is the free
hydrogen bonds, and various improved models of
binding energy, the more potent is the interaction.
the unbound state. AutoDock 4.2 applies a semi-
According to the table 1, among the total of
empirical free energy force field and grid-based
molecules tested, it was proved that A3 has the
docking to assess conformations during docking
lowest binding free energy (-11.96 kcal/mol), Van
process. Equation 3 represent the docking binding
der Waals energy (-13.14 kcal/mol) and also the
free energy, this formula automatically was
lowest inhibition constant (1.70 n M) and
computed by AutoDock 4.2 .
subsequently the most experimental affinity. It was
proved that after A3, B3 also has the lowest binding
Equation 3
free energy (-11.54 kcal/mol), the lowest Van der
Waals energy (-12.69 kcal/mol), the lowest inhibition constant (3.50 n M) and the most
In the above formula, the final intermolecular
experimental affinity. In other words, A3 and B3
energy is calculated with equation 4, so that the
have the highest interactions and the more potential
final intermolecular energy involves in van der
binding affinity for the enzyme binding site.
Special attention has been devoted to the
electrostatic contribution between the inhibitor and
substituent at thiazole ring. 2,4-dichlorophenyl
the protein binding site.
substitution leads to the highest potential binding
affinity at 2-(2-cycloheptylidenehydrazinyl) and
Equation 4
methyl cyclohexylidene hydrazinyl derivatives. It
has been found clearly that, in the presence of a
dichlorophenyl substituent in the 2,4 position, the potency of inhibitor was increased.
The active site is frequently known from crystal
Molecular docking was applied to describe and
distinguishing of active sites can play a central role
find out the binding sites in monoamine oxidase B.
in realizing protein function .
The final product of molecular docking, as the best
The docking results indicate that all inhibitors
docked structure was clustered to specify the
bind to monoamine oxidase B active site; active site
binding free energy and optimal docking energy
is a hydrophobic pocket that was surrounded by the
conformation. As well as we consider the molecular
aromatic and aliphatic residues. The active site of
docking results to elucidate their binding mode in
monoamine oxidase B constitutes of an entrance
the monoamine oxidase B.
cavity and substrate cavity; depending on the nature
Table 1 summarizes the docking results. In this
of the ligand, two cavities can be separated or
study the inhibition constant (Ki) and the RMSD
value for drug-like molecules were also determined.
Negative values of predicted free energies of
In structure-based design, the known or predicted
binding show that all inhibitors correctly docked to
shape of the binding site is used to optimize the
the crystal structure of the monoamine oxidase B.
inhibitor as a best fit to the receptor. As well as, the
Docking results also indicate that the contribution
orientations of these inhibitors in the active site are
of van der Waals interactions is greater than
very important, with their Ki values, for rational
electrostatic interactions so that, it can be
drug design. In most of the cases, careful
concluded that all of the inhibitors attached to a
observations of the figures divulge that inhibitor
hydrophobic binding site in monoamine oxidase B.
positioning in the active site sits reasonably well.
In other words, the non-polar interactions between
The binding manners and geometrical orientation of
monoamine oxidase B and inhibitors are the main
all compounds in the binding site were nearly
factor in the connectivity features and they are the
identical, hence proposing that all the inhibitors
dominant component contributing to the binding
have the same interactions with enzyme and
affinity. Among the molecules tested of A class, A3
occupied a common space in the receptor.
Hydrophobic cavity of binding site constitutes the
inner cavity of the active site, and comprises the
lowest binding free energy (-11.96 kcal/mol). As
residues such as Tyr 60, Leu171, Ile198, Gln206,
well as, among the molecules tested of B class, B3
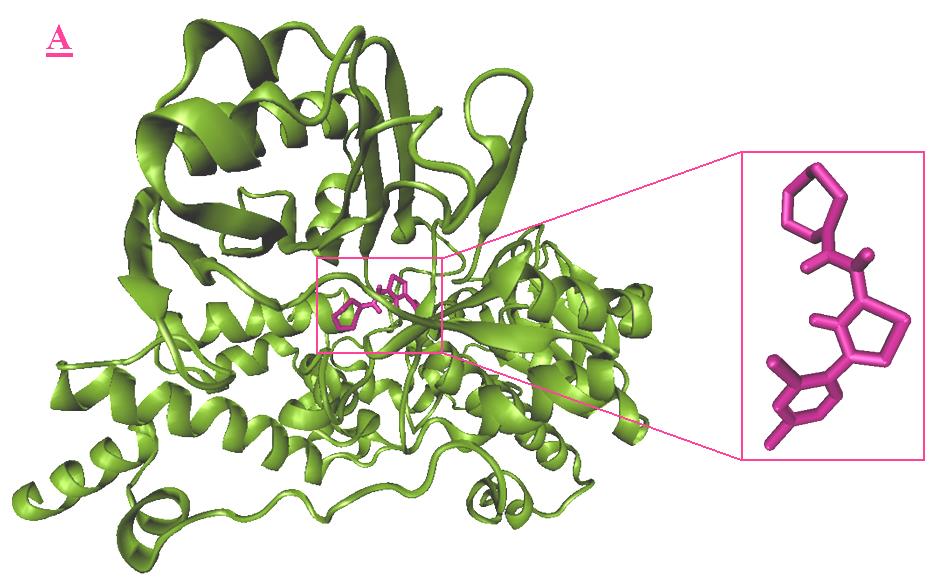
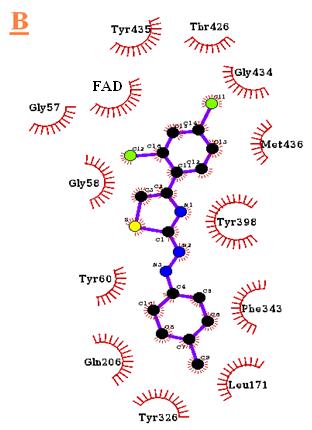
Tyr326, Leu328, Phe343, Tyr398, Tyr435. Fig 4
shows the lowest energy configuration of A3-
monoamine oxidase B complex. Observations of
demonstrated the lowest binding free energy (-
the docked conformation of A3 demonstrated
Molecular docking approach of monoamine oxidase B …
interactions with many residues; in this complex,
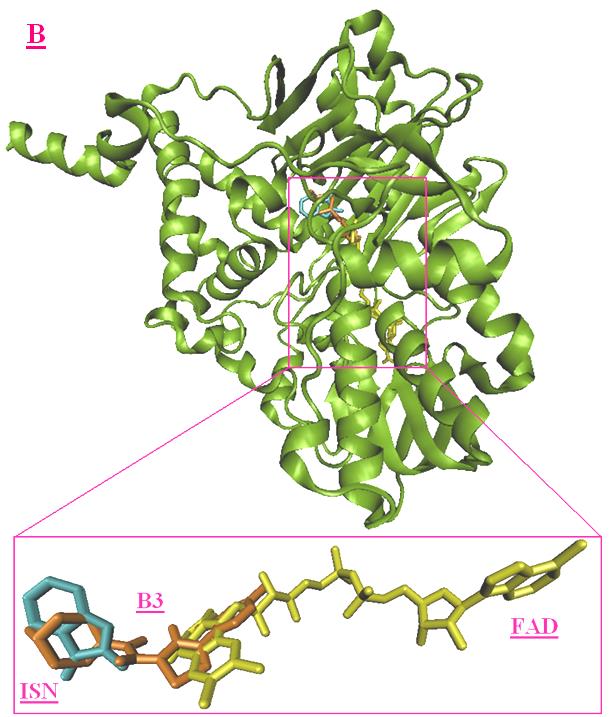
interactions. Fig 6-A shows the best virtual docking
A3 was located inside the cavity that comprising
pose of A3 and the superimposition of A3 and ISN,
the residues such as Gly57, Gly58, Leu171, Ile198,
and Fig 6-B shows the best virtual docking pose of
Gln206, Tyr326, Phe343, Tyr398, Thr426, Gly434,
B3 and the superimposition of B3 and ISN. In this
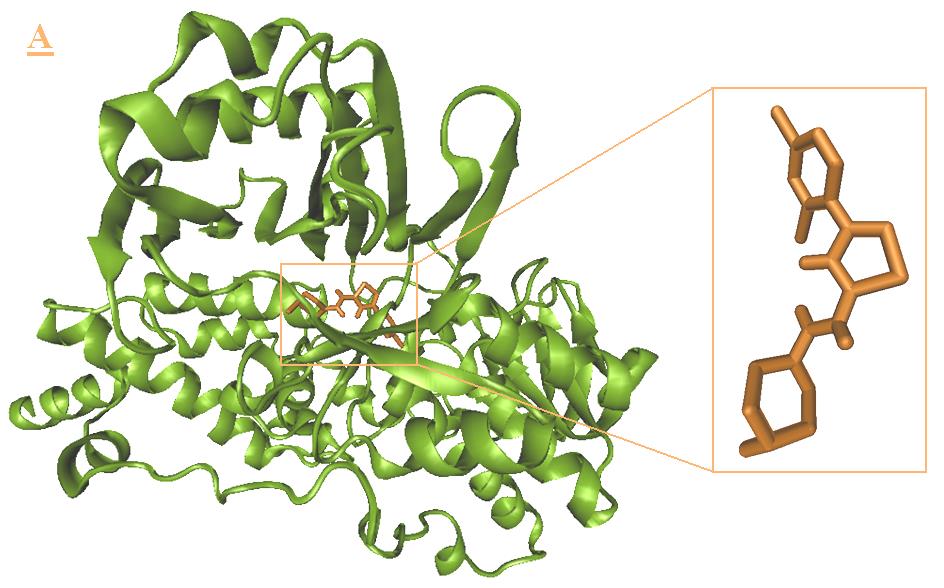
Tyr435, Met436. And Fig 5 shows the lowest
docked conformation, the A3 and B3 interact with
energy configuration of B3-monoamine oxidase B
flavin moiety of the FAD via a hydrogen bond and
complex, B3 was located inside the cavity that
show tight interactions with Gln206, Tyr326,
containing the residues such as Gly57, Gly58,
Phe343, Tyr398 and Tyr435 (Fig 6 A-B). For
Tyr60, Leu171, Gln206, Tyr326, Phe343, Tyr398,
superimposition of A3 and B3 with ISN, the indol
Thr426, Gly434, Tyr435, Met436.
ring is located between Tyr435 and Tyr398 in the
Other interactions proposed by the docking
hydrophobic cavity with an upright conformation to
consequences were the hydrophobic interactions of
flavin ring of FAD. Therefore, AutoDock 4.0
the inhibitors hydrophobic groups, as they were
viewed as reliable for docking A3 and B3, and
observed oriented towards the co-crystallized
related compounds into monoamine oxidase B.
ligand ISN, so that they have similar hydrophobic
Figure 3. X-ray crystal structure of monoamine oxidase B in complex with inhibitor ISN (purple) and FAD (red).
Table 1. Autodock's binding free energy derived from the docking studies on monoamine oxidase B.
Inhibitor Index
∆Gbinding
∆Ginter
∆Gtors
∆Gunbound
Abbreviations: ∆Gbinding, Estimated Free Energy of Binding (kcal/mol); ΔGvdw, vander Waals or Lennard–Jones potential factor of binding free energy (kcal/mol); ΔGelec, electrostatic factor of binding free energy (kcal/mol); ΔGinter, Gibbs free energy of binding (kcal/mol); ΔGtors, torsional energy of binding (kcal/mol); ∆Gunbound, unbound System's energy (kcal/mol); Ki, inhibition constant (nM); RMSD, reference root mean square deviation ; IC50 refers to the experimental predicted activity (mM). Refrence of inhibitor.
Journal of Cell and Molecular Research
Figure 4. Docking result of A3 (magenta) with monoamine oxidase B. The lowest energy configuration of A3-
monoamine oxidase B complex is demonstrated in VMD(A) and Ligplot (B) presentations. In Ligplot presentations (B),
carbons are in black, nitrogens in blue and oxygens in red.
Molecular docking approach of monoamine oxidase B …
Figure 5. Docking result of B3 (orange) with monoamine oxidase B. The lowest energy configuration of B3-
monoamine oxidase B complex is demonstrated in VMD(A) and Ligplot (B) presentations. In Ligplot presentations (B),
carbons are in black, nitrogens in blue and oxygens in red.
Journal of Cell and Molecular Research
Figure 6. Best virtual docking pose of A3 and B3. (A), superimposition of A3 (magenta) and FAD (red) and ISN
(purple); (B) superimposition of B3 (orange) and FAD (red) and ISN (purple).
Molecular docking approach of monoamine oxidase B …
Discussion
References
The target of this study was to carry out
1- Bortolato M., Chen K. and Shih J. C. (2008)
molecular docking to estimate the binding free
Monoamine oxidase inactivation: from pathophysiology
energies and inhibition constants of tested
to therapeutics. Advanced drug delivery reviews
monoamine oxidase B inhibitors and to compare
60:1527-1533. 2- Brooijmans N. 2009. Docking methods, ligand design
these computational results with those of the
and validating data sets in the structural genomics era. In
experimentally obtained results.
Structural Bioinformatics. J.G.a.P.E. Bourne, editor.
In the resent study, we employed computational
John Wiley & Sons.
approaches, such as molecular docking to estimate
3- Carroll R. T., Dluzen D. E., Stinnett H., Awale P. S.,
the binding free energy of two classes of
Funk M. O. and Geldenhuys W. J. (2011) Structure-
monoamine oxidase B inhibitors. Compare with the
van der Waals and electrostatic energies for these
thiazolidinedione-type compounds with monoamine
components showed a significant share of the van
oxidase B. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters
der Waals energies. Our results clearly showed that
non polar interactions play a significant role in
4- Chimenti F., Maccioni E., Secci D., Bolasco A., Chimenti P., Granese A., Befani O., Turini P., Alcaro S.
determining the binding free energy. Our findings
and Ortuso F. (2005) Synthesis, molecular modeling
studies, and selective inhibitory activity against
might demonstrate a crucial scaffold for the
monoamine oxidase of 1-thiocarbamoyl-3, 5-diaryl-4, 5-
development of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. All
dihydro-(1 H)-pyrazole derivatives. Journal of medicinal
inhibitors bind to monoamine oxidase B active site
chemistry 48:7113-7122.
and subsequently inhibit it. So that they have potent
5- Chimenti F., Secci D., Bolasco A., Chimenti P.,
affinity to the monoamine oxidase B and thus they
Bizzarri B., Granese A., Carradori S., Yanez M., Orallo
can behave like as the pharmaceutical agents.
F. and Ortuso F. (2009) Synthesis, Molecular Modeling,
Among the tested derivatives we preferred A3 and
and Selective Inhibitory Activity against Human
B3 as potent anti monoamine oxidase B agents.
Monoamine Oxidases of 3-Carboxamido-7-Substituted Coumarins†Journal of medicinal chemistry 52:1935-
Understanding, an atomic-level of the catalytic and
inhibition mechanisms of monoamine oxidase B
6- Chimenti F., Secci D., Bolasco A., Chimenti P.,
could assist to search for rationally-designed
Granese A., Befani O., Turini P., Alcaro S. and Ortuso F.
inhibitors of monoamine oxidase B, and would be
(2004) Inhibition of monoamine oxidases by coumarin-
of significant importance monoamine oxidase B
3-acyl derivatives: biological activity and computational
activity. In the present work, our purpose was to
study. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters
attain an agreement between the docking results
and experimental data. We discovered good
7- Chimenti F., Secci D., Bolasco A., Chimenti P.,
relationship between the estimated results and
Granese A., Carradori S., Befani O., Turini P., Alcaro S.
experimental data. The selective information from
and Ortuso F. (2006) Synthesis, molecular modeling studies, and selective inhibitory activity against
this work is crucial for the rational drug design of
monoamine oxidase of N-bis [2-oxo-2-H-benzopyran]-3-
more potent and selective monoamine oxidase B
carboxamides. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters
inhibitors based on the 8-benzyloxycaffeine
scaffold. Such observations can also help to study
8- Coelho Cerqueira E., Netz P. A., Diniz C., Petry do
8-benzyloxycaffeine, by increased metabolism of
Canto V. and Follmer C. (2010) Molecular insights into
biogenic amines within some key areas of the
human monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibition by 1, 4-
central nervous system, as an effective scaffold for
naphthoquinone: Evidences for menadione (vitamin K3)
rational design of novel and potential drugs against
acting as a competitive and reversible inhibitor of MAO.
diseases precipitated.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 19:7416-7424.
9- Delogu G., Picciau C., Ferino G., Quezada E., Podda G., Uriarte E. and Vina D. (2011) Synthesis, human
Note: All the figures are color in online version.
monoamine oxidase inhibitory activity and molecular
docking studies of 3-heteroarylcoumarin derivatives.
European journal of medicinal chemistry 46:1147-1152.
10- Froimowitz M. (1993) HyperChem: a software
I thank to the Golestan University for their
package for computational chemistry and molecular
financial support to perform this work.
modeling. BioTechniques 14:1010-1013.
11- Geldenhuys W. J., Funk M. O., Van der Schyf C. J. and Carroll R. T. (2012) A scaffold hopping approach to
identify novel monoamine oxidase B inhibitors.
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 22:1380-1383.
Journal of Cell and Molecular Research
12- Goodsell D. S. (2009) Computational docking of
26- Scheer M., Grote A., Chang A., Schomburg I.,
biomolecular complexes with AutoDock. Cold Spring
Munaretto C., Rother M., Sohngen C., Stelzer M., Thiele
Harbor protocols 2009:pdb prot5200.
J. and Schomburg D. (2011) BRENDA, the enzyme
13- Harkcom W. T. and Bevan D. R. (2007) Molecular
information system in 2011. Nucleic acids research
docking of inhibitors into monoamine oxidase B.
Biochemical and biophysical research communications
27- Strydom B., Malan S. F., Castagnoli N., Bergh J. J.
and Petzer J. P. (2010) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase
14- Herraiz T. and Chaparro C. (2005) Human
by 8-benzyloxycaffeine analogues. Bioorganic &
monoamine oxidase is inhibited by tobacco smoke: b-
medicinal chemistry 18:1018-1028.
carboline alkaloids act as potent and reversible
28- Taylor R. D., Jewsbury P. J. and Essex J. W. (2002)
inhibitors. Biochemical and Biophysical Research
A review of protein-small molecule docking methods.
Communications 326:378–386.
Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design 16:151–
15- Ivanciuc O. (1996) HyperChem Release 7 for
Windows. Journal of chemical information and computer
29- Van der Walt E. M., Milczek E. M., Malan S. F.,
sciences 36:612-614.
Edmondson D. E., Castagnoli Jr N., Bergh J. J. and
16- Jensen S. B., Olsen A. K., Pedersen K. and
Petzer J. P. (2009) Inhibition of monoamine oxidase by (
Cumming P. (2006) Effect of monoamine oxidase
E)-styrylisatin analogues. Bioorganic & medicinal
inhibition on amphetamine evoked changes in dopamine
chemistry letters 19:2509-2513.
receptor availability in the living pig: A dual tracer PET
30- Wu G., Robertson D. H., Brooks C. L. and Vieth M.
study with [11C] harmine and [11C] raclopride. Synapse
(2003) Detailed analysis of gridbased molecular
docking: A case study of C-DOCKER. A CHARM
17- Kitchen D. B., Decornez H. l. n., Furr J. R. and
based MD docking algorithm. Journal of computational
Bajorath J. r. (2004) Docking and scoring in virtual
chemistry 24:1549-1562.
screening for drug discovery: methods and applications.
Nature reviews Drug discovery 3:935-949.
18- Lewis A., Miller J. H. and Lea R. A. (2007)
Neurotoxicology 28:182-195.
19- Luhr S., Vilches-Herrera M., Fierro A., Ramsay R.
R., Edmondson D. E., Reyes-Parada M., Cassels B. K.
and Iturriaga-Vasquez P. (2010) 2-Arylthiomorpholine
derivatives as potent and selective monoamine oxidase B
inhibitors. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 18:1388-
20- Morris G. M., Huey R., Lindstrom W., Sanner M. F.,
Belew R. K., Goodsell D. S. and Olson A. J. (2009)
AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking
computational chemistry 30:2785-2791.
21- Morris G. M., Huey R. and Olson A. J. (2008) Using
AutoDock for ligand-receptor docking. Current protocols
in bioinformatics / editoral board, Andreas D. Baxevanis
. [et al.] Chapter 8:Unit 8 14.
22- Mu L.-H., Wang B., Ren H.-Y., Liu P., Guo D.-H.,
Wang F.-M., Bai L. and Guo Y.-S. (2012) Synthesis and
inhibitory effect of piperine derivates on monoamine
oxidase. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters.
23- Nagatsu T. (2004) Progress in monoamine oxidase
(MAO) research in relation to genetic engineering.
Neurotoxicology 25:11-20.
24- Oreland L. (2004) Platelet monoamine oxidase,
personality and alcoholism: the rise, fall and
resurrection. Neurotoxicology 25:79-89.
25- Reniers J., Meinguet C., Moineaux L., Masereel B.,
Vincent S. P., Frederick R. and Wouters J. (2011)
Synthesis and inhibition study of monoamine oxidase,
indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase and tryptophan 2, 3-
dioxygenase by 3, 8-substituted 5 H-indeno [1, 2 c]
pyridazin-5-one derivatives. European journal of
medicinal chemistry 46:6104-6111.
Source: http://jcmr.um.ac.ir/index.php/biology/article/download/20870/4756
29 novembre 2012 Agora Morris et Rosalind 16 h 45 Accueil 17 h 10 à 17 h 25 Mots de bienvenue • Pierre Moreau, doyen de la Faculté• Brian White-Guay, directeur du BSBP• Marc Perreault, directeur de la Maîtrise en pharmacothérapie avancée 17 h 25 à 19 h 30 Découverte des affiches Curieux de recherche ? Cheminement honor
bei Erwachsenen Anleitung zur medikamentösen Tumorschmerztherapie (Überarbeitet von Dr. Beekhchand Permar) Pflegeinterventionen in der Schmerztherapie Herausgeber: Arbeitsgruppe Schmerztherapie im Onkologischen Zentrum Westpfalz für die Arbeitsgruppe: Prof. Dr. Ch. Madler, Anästhesiologie Prof. Dr. H. Link, Medizinische Klinik














